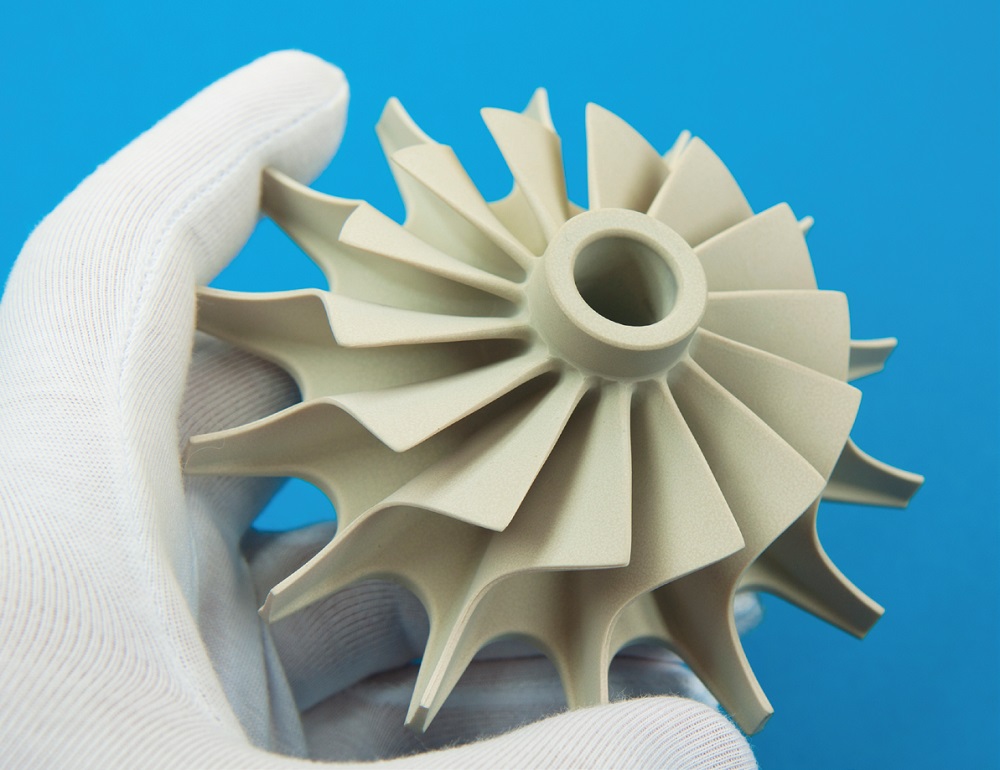
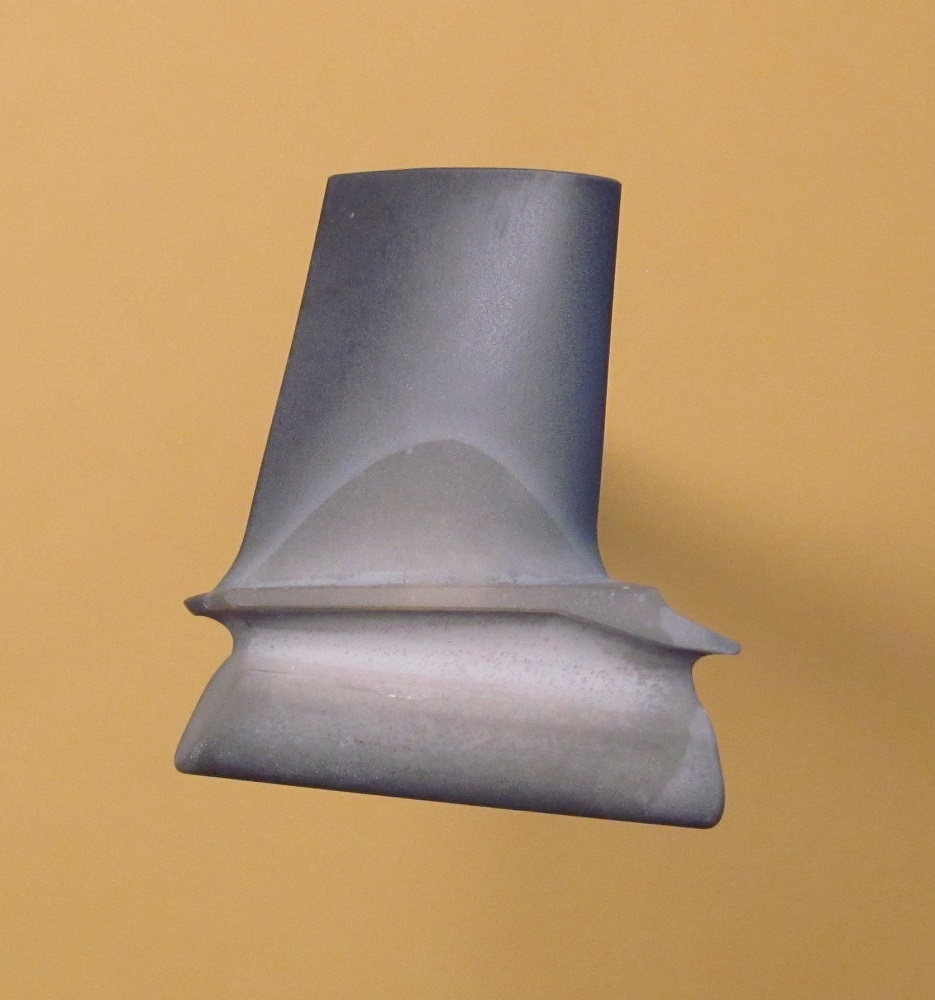
In addition to various electrical applications, advanced ceramics are mainly used in gas turbines as thermal insulation. In aircraft engines and stationary gas turbines, they are used in the form of tiles or coatings on metallic components and thus enable the fuel gas temperature to be raised or cooling to be reduced. Both lead to an increase in efficiency and thus to a reduction in fuel consumption and pollutant emissions.
The efficiency of engines and gas turbines can be increased even further with all-ceramic components. Silicon nitride is particularly suitable for this purpose. Si3N4 has outstanding thermomechanical properties – even at very high temperatures.
Services offered
- Development of specifically adapted ceramic materials for high-temperature applications as well as for oxidative and corrosive atmospheres and media
- Application-oriented characterization of materials and components
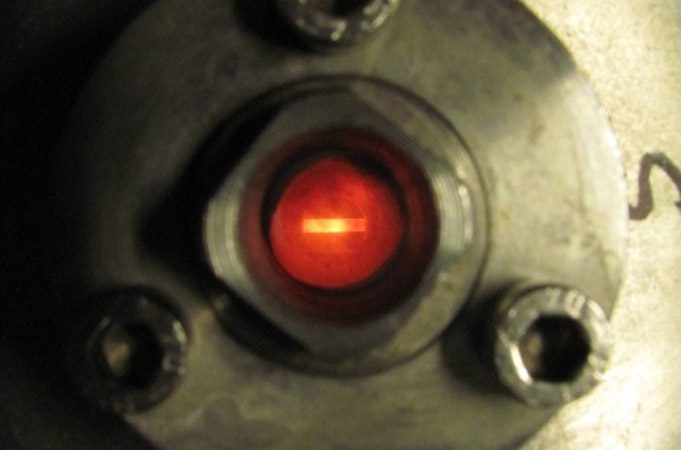
- Mechanical testing from room temperature to high temperatures (1550 °C)
- Oxidation test up to 1600 °C
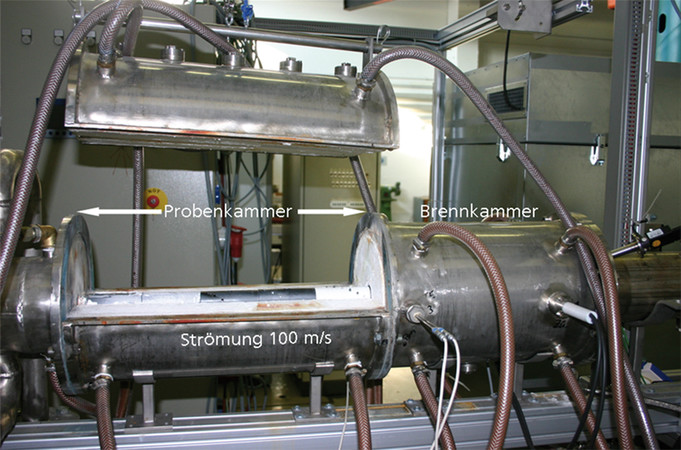
- Hot gas corrosion test up to 1450 °C under gas turbine-like conditions
- Prototype development and tests under near-application conditions


