
Special measuring methods for power electronics
Current research

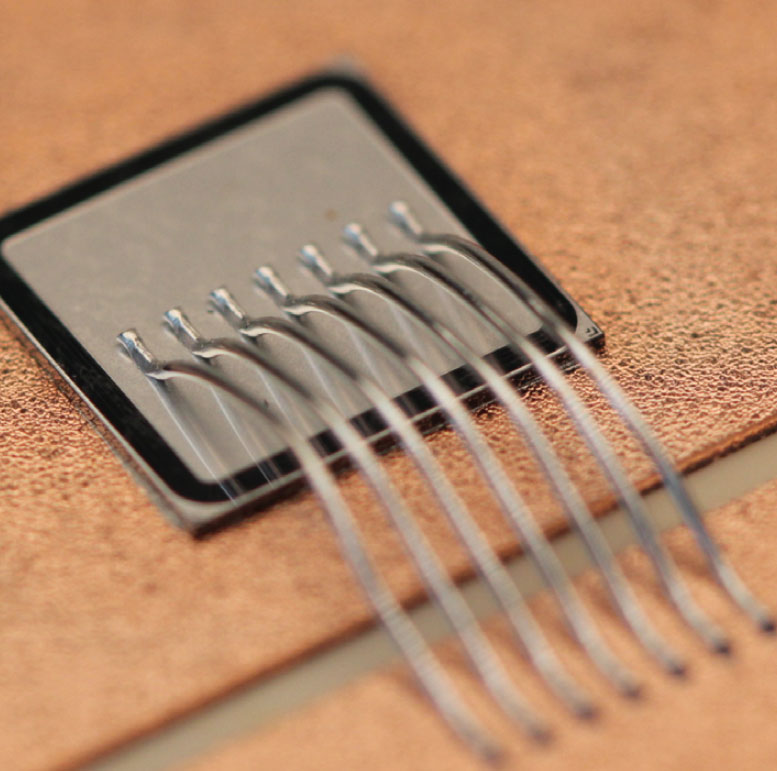
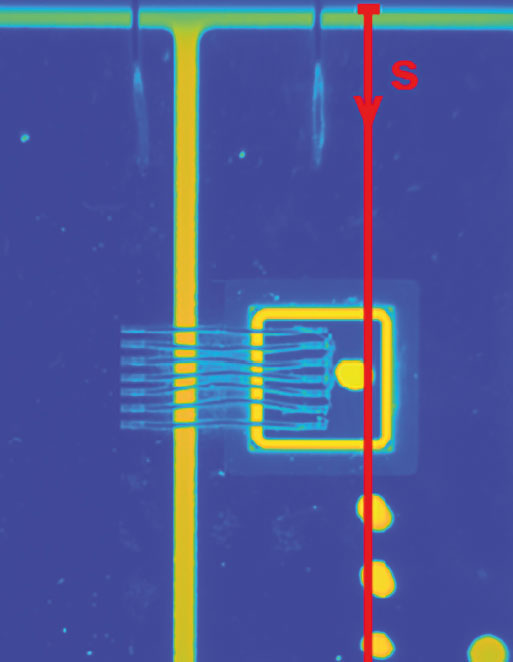
The range of applications for power electronic modules will continue to grow significantly in the coming years. This development is driven by the high demand in e-mobility and renewable energies. The use of ceramic substrates in power electronic modules is state of the art. This is due to the high electrical insulation strength of technical ceramics combined with their good thermal conductivity. With the use of fast-switching, wide bandgap power semiconductors, such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), the requirements on electrical insulation strength, mechanical stability, and heat dissipation capabilities of ceramic circuit carriers in power electronic modules are increasing. Application-specific measuring methods are refined at Fraunhofer IKTS to characterize the different assembly stages and components.
Partial discharge measurement
Partial discharge measurement is, as a non-destructive measurement method, well suited for the characterization of the metal-ceramic composite. Internal defects, such as delamination, conchoidal fractures or cavities, are revealed in the form of local partial breakdowns and thus as measurable current peaks in the supply power line. Since both recording and evaluation of the stochastic measurement data require a lot of time and computing effort, a highly automated measurement system is used. The data evaluation is developed further using machine learning based on the visualization methods currently used. The aim is to make the experience gained generally applicable in a data model. In addition to metal-ceramic or polymer substrates, future measurements will also focus on molding compounds and more complex structures.
Infrared thermography
Infrared thermography (IR thermography) is an effective non-destructive and non-contact measurement method. It enables recording heat distribution dynamically. For instance, particularly temperature-stressed areas can be identified locally and temperature gradients on ceramic circuit carriers equipped with bare dies can be recorded. At IKTS, there is extensive experience with ceramic circuit carriers, such as
- DCBs (direct copper bonding)
- AMBs (active metal brazing)
- Copper and silver thick-film substrates.
The measurements focus on thermal conductivity, efficiency and thermal capacity. The entire measurement system can be flexibly expanded. Additional temperature sensors can provide further information on the heat flow and thus enable comprehensive classification of the thermal behavior. A wide range of current sources is available for impressing electrical power into the sample structures and devices. The setup can be adapted to suit user-specific measurement requirements. The thermal power can be dissipated passively to the ambient air or actively via a cooling circuit with thermostat. Depending on the requirements, the thermostat can also be used as a heater.
Supported by

