CCU/CCS (Carbon Capture and Utilization/Storage) technologies aim to capture CO2 from industrial waste gases and use it as a raw material or store it geologically. This makes it possible to avoid CO2 emissions and at the same time expand the raw material base by replacing fossil carbon sources.
Fraunhofer IKTS takes numerous factors into account in its techno-economic evaluation of projects to capture CO2, including
- Avoidance of emission costs (in the EU ETS)
- Proceeds from the sale of CO2 as a raw material
- Costs for CO2 capture and transportation (investment and operating costs)
- Perspective: certificates for CO2 removal (negative emissions)
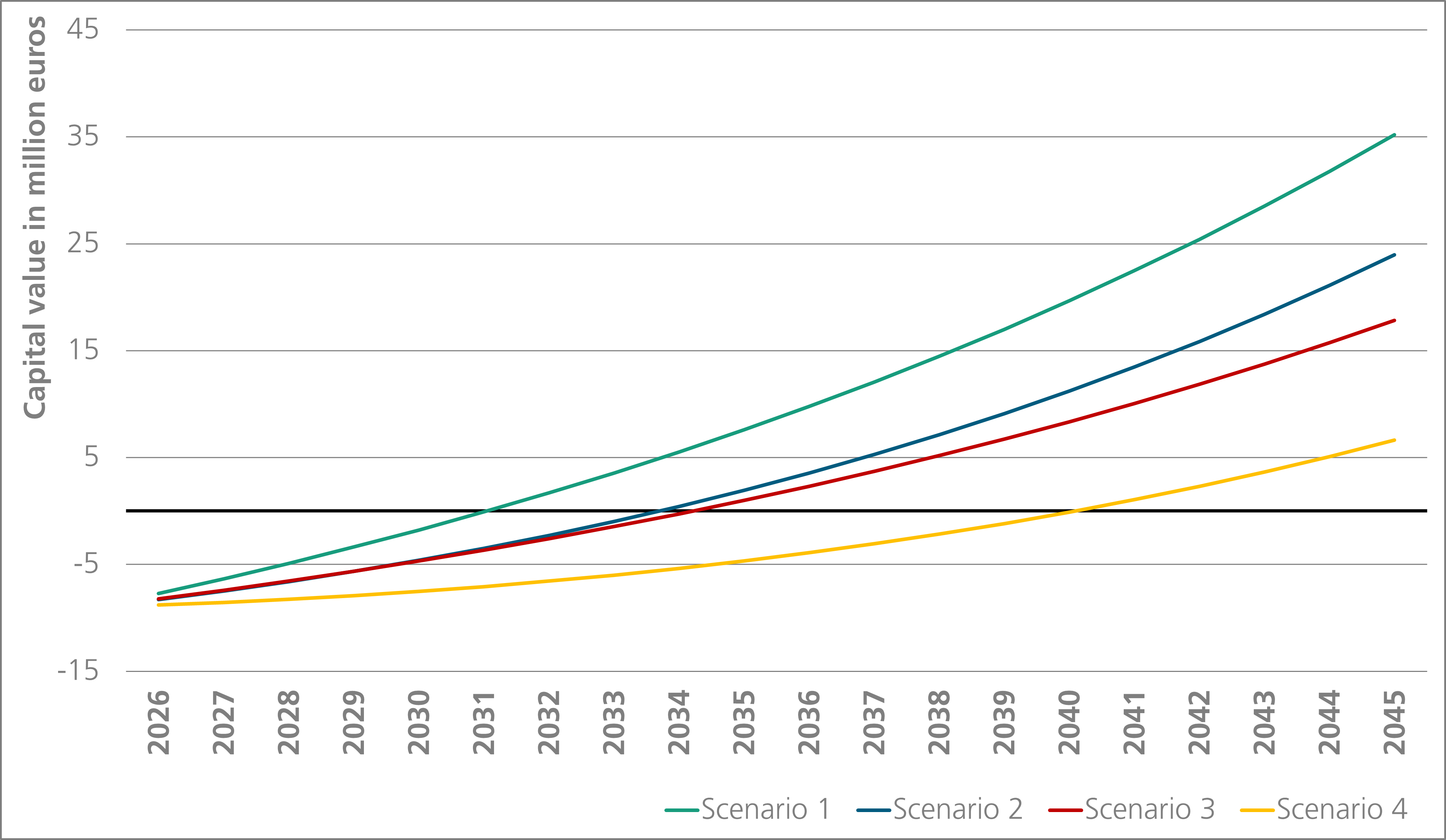
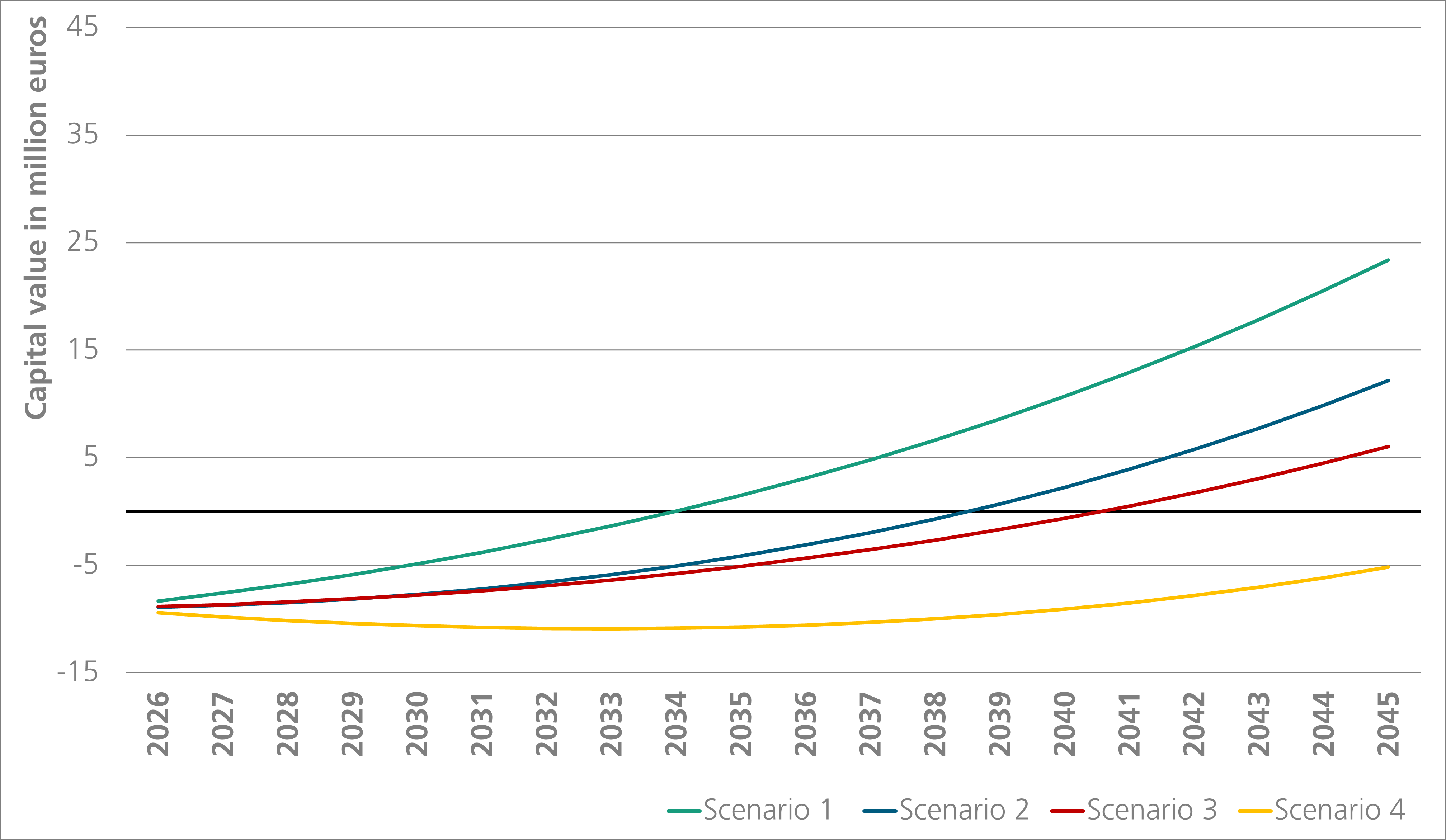
The following example shows the techno-economic assessment of CO2 capture at a waste incineration plant using amine scrubbing. The following four scenarios were considered:
| SCENARIO | Energy prices | Emission costs |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Low (Electricity: 50 €/MWh, Heating: 12 €/GJ) | High (130 €/t CO2) |
| 2 |
High (Electricity: 120 €/MWh, Heating: 24 €/GJ) | High (130 €/t CO2) |
| 3 |
Low (Electricity: 50 €/MWh, Heating: 12 €/GJ) | Low (80 €/t CO2) |
| 4 |
High (Electricity: 120 €/MWh, Heating: 24 €/GJ) | Low (80 €/t CO2) |