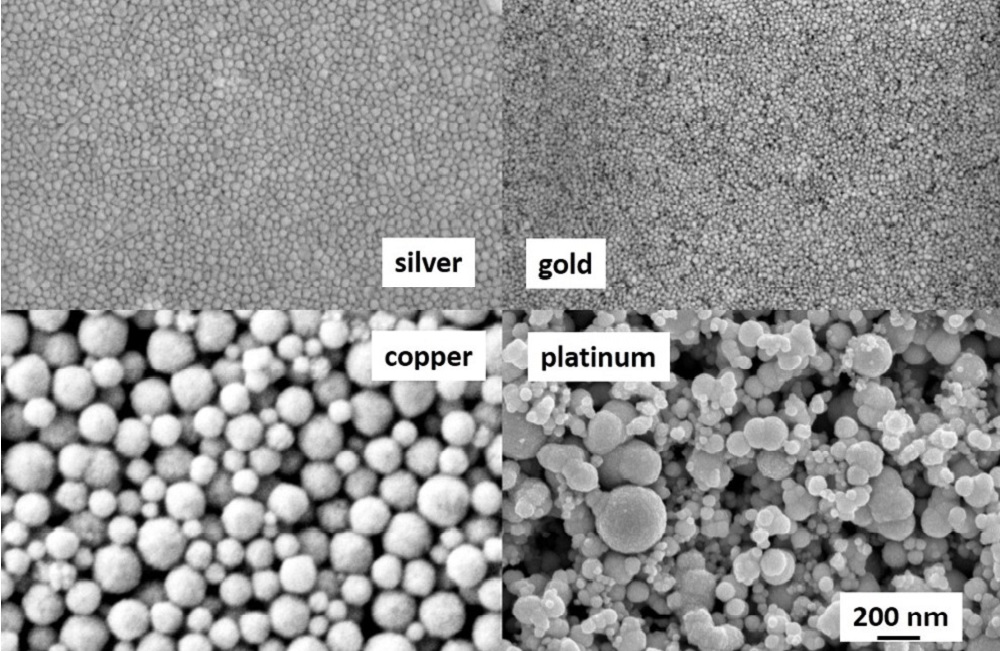
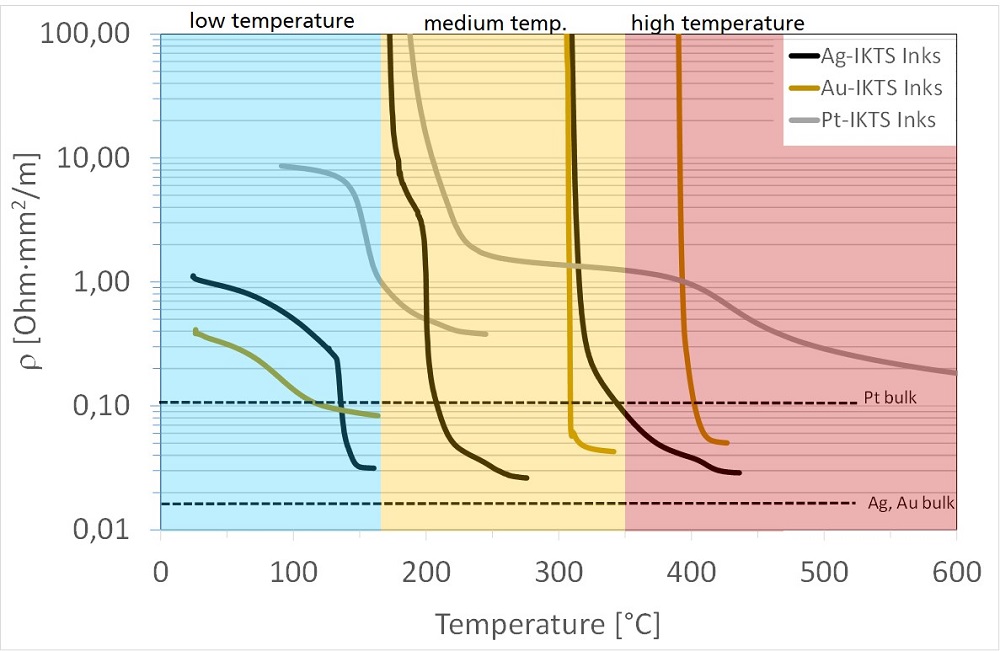
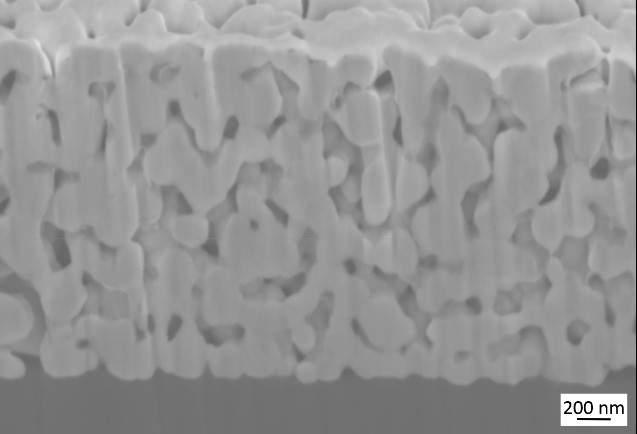
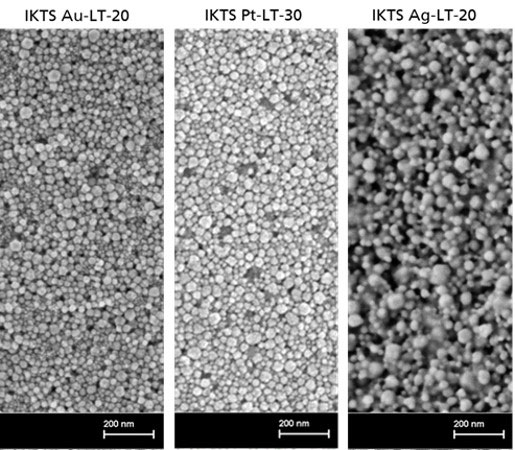
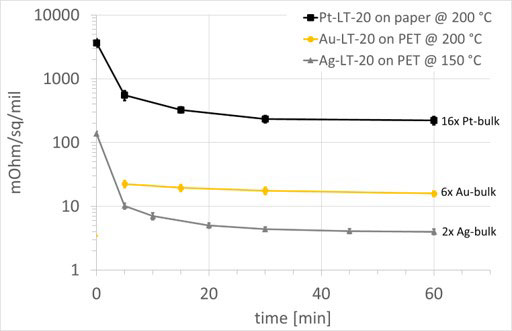
Veröffentlichungen von Forschungsarbeiten unserer Kunden sowie der IKTS-Arbeitsgruppe (hervorgehoben), die auf unserer Tintenentwicklung basieren:
2025
[75] A. Sharipova, A. Böhme, M. Fritsch, M. Ahlhelm „A concept for functional bioceramics with embedded metallization using cold sintering”, Open Ceramics 21 (2025) 100716. DOI 10.1016/j.oceram.2024.100716.
2024
[74] C. Voigt, M. Fritsch, M. Vinnichenko, M. Kusnezoff „Tintenstrahlgedruckte AMR-Sensoren und AMR-Sensorarrays auf polymeren Substraten“, 17. Dresdner Sensor-Symposium 2024. Download from https://www.ama-science.org/proceedings/details/5822. DOI 10.5162/17dss2024/P41.
[73] C. Voigt, S. Mosch, E.S. Oliveros-Mata, D. Makarov, C. Schubert “Printed Anisotropic Magnetoresistive Sensors on Flexible Polymer Foils”, Proceedings 2024, 97, 177. DOI 10.3390/proceedings2024097177.
[72] K. Vora, N. Kordas, K. Seidl „Fabrication and characterization of inkjet-printed interdigitated electrodes for non-faradaic electrochemical detection of uromodulin in urine”, Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research 46 (2024) 100715. DOI 10.1016/j.sbsr.2024.100715.
[71] I. Lopez Carrasco, G. Cuniberti, J. Opitz, N. Beshchasna “Evaluation of Transducer Elements Based on Different Material Configurations for Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensors”, Biosensors 2024, 14, 341. DOI 10.3390/bios14070341.
2023
[70] P. Bischoff, A. V. Carreiro, C. Schuster and T. Härtling “Quantifying the Displacement of Data Matrix Code Modules: A Comparative Study of Different Approximation Approaches for Predictive Maintenance of Drop-on-Demand Printing Systems”, J. Imaging 9, 125, 2023. DOI 103390/jimaging9070125.
[69] A. Arché-Núñez, P. Krebsbach, B. Levit, D. Possti, A. Gerston, T. Knoll, T. Velten, C. Bar-Haim, S. Oz, S. Klorfeld-Auslender, G. Hernandez-Sosa, A. Mirelman and Y. Hanein “Bio-potential noise of dry printed electrodes: physiology versus the skin-electrode impedance”, Physiol. Meas. 44, 095006., 2023. DOI 10.1088/1361-6579/acf2e7.
[68] E. Hollinger, M. Fritsch, S. Mosch, N. Trofimenko “Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of gold nanoparticles for inkjet inks”, Poster presented at Large-area, Organic & Printed Electronics Convention - LOPEC 2023, München Germany (1.-2.3.2023).
[67] Boris Goikhman, Moshe Avraham, Sharon Bar-Lev, Sara Stolyarova, Tanya Blank and Yael Nemirovsky “A Novel Miniature and Selective CMOS Gas Sensor for Gas Mixture Analysis—Part 3: Extending the Chemical Modeling”, Micromachines, 14, 270, 2023. DOI: 10.3390/mi14020270.
[66] S. Jungginger “Benetzungsverhalten in Zusammenhang mit der Polarität und Bestimmung der Latenzzeit von Goldtintenvariationen gedruckt mit dem Dimatix DMP Samba Inkjet-Druckkopf”, Bachelorarbeit 03.04.2023, Hochschule für Technik, Wirtschaft und Kultur Leipzig, Fakultät Informatik und Medien, Studiengang Digitale Print-Technologien.
[65] M. Fritsch, K. Hariharan, F. Stracke, M. Vinnichenko, I. Meiser, S. Mosch, J.C. Neubauer, R. Ruff, R. Le Harzic, S. Wagner, T. Knoll “HeartBeat - Inkjet printed platform on polymer foil for the functional monitoring of cardiomyocyte cells”, presentation held at Large-area, Organic and Printed Electronics Convention – LOPEC Congress, Munich Germany 02.03.2023.
2022
[64] P. Bischoff, A. V. Carreiro, C. Kroh, C. Schuster and T. Härtling “En route to automated maintenance of industrial printing systems: digital quantification of print-quality factors based on induced printing failure”, Journal of Sensors and Sensor Systems, Volume 11 (2), pp.277–285, 2022. DOI 10.5194/jsss-11-277-2022.
[63] M. Fritsch, S. Mosch, M. Vinnichenko, M. Kusnezoff, Z. Kiaee and R. Keding “Inkjet printable boron-doped silicon particle ink”, poster presented at Freiberg Silicon Days, Freiberg Germany (9.-10.06.2022).
[62] E. S. Oliveros-Mata, C. Voigt, S. G. Santiago Cañón-Bermúdez, Y. Zabila, G. Valdez Garduño, M. Nestor, M. Fritsch, S. Mosch, M. Kusnezoff, J. Fassbender, M. Vinnichenko, and D. Makarov “Dispenser Printed Bismuth‐Based Magnetic Field Sensors with Non‐Saturating Large Magnetoresistance for Touchless Interactive Surfaces”, Advanced Materials Technologies by A. DeMello [ed.] (ETH Zürich) J. Rogers [ed.] (Northwestern University) Z. L. Wang [ed.] (School of Materials Science and Engineering). - Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. - 2365-709X (E-ISSN), 2022.
[61] M. H. Fakhr, N. Beshchasna, S. Balakin, I. Lopez Carrasco, A. Heitbrink, F. Göhler, N. Rösch, J. Opitz “Cleaning of LTCC, PEN, and PCB Au electrodes towards reliable electrochemical measurements”, Scientific Reports, 12:20431, 2022. Doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-23395-3.
[60] Fabian Loepthien “Benetzungsverhalten von Silber- und Goldnanotinten auf Polymersubstraten : Einfluss des Benetzungsverhaltens auf die Qualität und Schichthaftung Inkjet gedruckter Leitbahnen”, Fraunhofer IKTS / TU Dresden. Diploma Thesis, Dresden Germany, 2022.
[59] E. S. Oliveros-Mata, C. Voigt, G. S. Cañón Bermúdez, Y. Zabila, N. M. Valdez-Garduño, M. Fritsch, S. Mosch, M. Kusnezoff, J. Fassbender, M. Vinnichenko and D. Makarov “Dispenser Printed Bismuth-Based Magnetic Field Sensors with Non-Saturating Large Magnetoresistance for Touchless Interactive Surfaces”, Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2200227, Doi.org/10.1002/admt.202200227.
[58] M. A. U. Khalid, K. Hwan Kim, A. R. C. Salih, K. Hyun, S. Hyuk Park, B. Kang, A. M. Soomro, M. Ali, Y. Jun, D. Huh, H. Cho and K. Hyun Choi “High performance inkjet printed embedded electrochemical sensors for monitoring hypoxia in a gut bilayer microfluidic chip”, Lab Chip, 22, 1764, 2022. DOI: 10.1039/d1lc01079d.
2021
[57] T. Velten, H. Schuck, T. Knoll, S. Wagner, D. Volk, Y. Hanein, T. Hendler, M. Farah and L. Asfour “Nano-based portable electronics for the diagnosis of mental disorders and functional restoration, production technologies and devices”, Results of the German-Israeli collaborative project NanoEDGE, Publisher Fraunhofer IBMT Sulzbach Germany, 2021. DOI: 10.24406/publica-fhg-301341.
[56] Moritz Fritz Langer “Printing and photonic post-processing of soft-magnetic structures combined with electrical conductors”, KU Leuven / Fraunhofer IKTS / TU Dresden. Master Thesis, 2021.
[55] H. M. U. Farooqi, B. Kang, M. A. U. Khalid, A. R. C. Salih K. Hyun, S. Hyuk Park, D. Huh and K. Hyun Choi “Real‑time monitoring of liver fibrosis through embedded sensors in a microphysiological system”, Nano Convergence 8:3, 2021. Doi.org/10.1186/s40580-021-00253-y.
[54] N. Samotaev, K. Oblov, P. Dzhumaev, M. Fritsch, M., S. Mosch, M. Vinnichenko, N. Trofimenko, C. Baumgärtner, F.-M. Fuchs, L. Wissmeier “Combination of Ceramic Laser Micromachining and Printed Technology as a Way for Rapid Prototyping Semiconductor Gas Sensors”, Micromachines, 12, 1440, 2021. DOI: 10.3390/mi12121440.
[53] M. Fritsch, A. Kabla, R. Zichner, D. Mitra, N. Shaly, S. Kapadia, L. Wissmeier,N. Samotaev “Digital Manufacturing Technologies for the Development of Smart Sensors and Electronics for Agro-Industrial Systems”, Research and development report of the MANUNET ERA-NET collaboration project „DigiMan“, 28.04.2021. http://publica.fraunhofer.de/dokumente/N-634398.html. DOI: 10.24406/ikts-n-634398.
[52] L. Petani, V. Wehrheim, L. Koker, M. Reischl, M. Ungerer, U. Gengenbach and C. Pylatiuk ”Systematic assessment of the biocompatibility of materials for inkjet-printed ozone sensors for medical therapy”, Flexible and Printed Electronics, Volume 6, Number 4, 2021. DOI: 10.1088/2058-8585/ac32ab.
[51] M. Zea, R. Texidó, R. Villa, S. Borrós, G. Gabriel “Specially Designed Polyaniline/Polypyrrole Ink for a Fully Printed Highly Sensitive pH Microsensor”, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.; 13(28), pp.33524-33535, 2021. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.1c08043.
[50] P. Kuberský, J. Navrátil, T. Syrový, P. Sedlák, S. Nešpurek, A. Hamácek “An Electrochemical Amperometric Ethylene Sensor with Solid Polymer Electrolyte Based on Ionic Liquid”, Sensors, 21, 711, 2021. DOI: 10.3390/s21030711.
2020
[49] M. Fritsch, S. Mosch, M. Vinnichenko, N. Trofimenko, M. Kusnezoff, F.-M. Fuchs, L. Wissmeier, N. Samotaev, M. Etrekova, D. Filipchuk “Printed Miniaturized Platinum Heater on Ultra-Thin Ceramic Membrane for MOX Gas Sensors”, International Youth Conference on Electronics, Telecommunications and Information Technologies, 2020-11-28, Vol.255, p.97-103, Springer International Publishing, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-58868-7_11.
[48] M. Fritsch, S. Mosch, M. Vinnichenko, N. Trofimenko, M. Kusnezoff, F.M. Fuchs, L. Wissmeier, N. Samotaev, K. Oblov “Printed Miniaturized Platinum Heater on Ultra-Thin Ceramic Membrane for Mox Gas Sensors” ECS Meeting Abstracts, Vol. MA2020-01, IMCS 03: Electrochemical and Metal Oxide Sensors, 2020. DOI: 10.1149/MA2020-01282125mtgabs.
[47] N. Samotaev, K. Oblov, A. Gorshkova, M. Fritsch, S. Mosch, M. Vinnichenko, N. Trofimenko, M. Kusnezoff, F.-M. Fuchs, L. Wissmeier “Ceramic microhotplates for low power metal oxide gas sensors”, Materials Today: Proceedings, Volume 30, Part 3, Pages 448-451, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2019.12.394.
[46] M. Avraham, S. Stolyarova, T. Blank, S. Bar‐Lev, G. Golan, Y. Nemirovsky “A Novel Miniature and Selective CMOS Gas Sensor for Gas Mixture Analysis—Part 2: Emphasis on Physical Aspects” Micromachines 11(6), pp.587, 2020. DOI: 10.3390/mi11060587.
[45] D. Shlenkevitch, S. Stolyarova, T. Blank, I. Brouk, Y.i Levi and Y. Nemirovsky “Reducing Food Waste with a Tiny CMOS-MEMS Gas Sensor, Dubbed GMOS”, Eng. Proc., 2, 36, 2020. DOI 10.3390/ecsa-7-08190.
[44] D. Shlenkevitch, S. Stolyarova, T. Blank, I. Brouk, Y. Nemirovsky “Novel Miniature and Selective Combustion-Type CMOS Gas Sensor for Gas-Mixture Analysis—Part 1: Emphasis on Chemical Aspects” Micromachines 11(4), pp. 345, 2020. DOI: 10.3390/mi11040345.
2019
[43] M. Fritsch, S. Mosch, N. Trofimenko, V. Sauchuk, M. Vinnichenko, M. Kusnezoff, N. Beshchasna, M. Draz, L. Röhmhildt and J. Opitz “Nanotinten für den Inkjet-Druck biomedizinischer Sensorkomponenten”, 14. Dresdner Sensor-Symposium, Dresden (2.-4.12.2019), DOI 10.5162/14dss2019/5.4.
[42] M. Vinnichenko, N. Trofimenko, V. Sauchuk, S. Mosch, M. Fritsch, M. Kusnezoff, J.-I. Mönch, B. Canon, S. Gilbert and D. Makarov “Novel flexible magnetic field sensors prepared by combining screen printing and millisecond diode laser post-processing”, Poster presented at 14. Dresdner Sensor-Symposium, Dresden Germany (2.-4.12.2019).
[41] A. Habermehl “Rolle-zu-Rolle-Herstellung von mikrofluidischen Analysesystemen basierend auf der oberflächenverstärkten Ramanspektroskopie”, PhD-Thesis, KIT Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology (ETIT) of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), 18.03.2019.
[40] S. Demuru, A. Marette, W. Kooli, P. Junier and D. Briand, "Flexible Organic Electrochemical Transistor with Functionalized Inkjet-Printed Gold Gate for Bacteria Sensing," 2019 20th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems & Eurosensors XXXIII (TRANSDUCERS & EUROSENSORS XXXIII), pp. 2519-2522, 2019. DOI: 10.1109/TRANSDUCERS.2019.8808309.
[39] B. Cruz, A. Albrecht, P. Eschlwech, E. Biebl „Inkjet printing of metal nanoparticles for green UHF RFID tags“ Adv. Radio Sci., 17, 119–127, 2019. DOI: 10.5194/ars-17-119-2019.
[38] S. Khan and D. Briand “All-printed low-power metal oxide gas sensors on polymeric substrates”, Flex. Print. Electron. 4, 015002, 2019. DOI: doi.org/10.1088/2058-8585/aaf848.
[37] N. Samotaev, K. Oblov, A. Gorshkova, M. Fritsch, S. Mosch, F.M. Fuchs, L. Wissmeier, M. Vinnichenko, N. Trofimenko, M. Kusnezoff „Ceramic microhotplates for low power metal oxide gas sensors“, International Scientific Conference “Materials Science: Composites, Alloys and Materials Chemistry” (MS-CAMC), St. Petersburg Russia, 20.-21.11.2019.
[36] S. Kapadia, M. Fritsch, A. Kabla, F.M. Fuchs, E. Bilbao, L. Monsalve, J. Fossati, K.Y. Mitra, A. Trul, E. Agina, S. Ponomarenko „The development & fabrication of the all inkjet printed electronic devices using novel functional materials suitable for various sensing applications in the field of printed and flexible electronic“, Printing for Fabrication conference, San Francisco USA, 29.09-03.10.2019.
[35] N. Samotaev, K. Oblov, A. Ivanova, A. Gorshkova, B. Podlepetsky „Rapid Prototyping of MOX Gas Sensors in Form-factor of SMD Packages“, 31st International Conference on Microelectronics (MIEL), Nis Serbia, 16.-18.09.2019.
[34] M. Fritsch, S. Mosch, N. Trofimenko, V. Sauchuk, M. Vinnichenko, M. Kusnezoff, N. Beshchasna, M.S. Draz “Material inks for inkjet printed biomedical sensor applications“,30th Annual Conference of the European Society for Biomaterials (ESB), Dresden Germany, 09.-13.09.2019. DOI 10.5162/14dss2019/5.4. Available from https://www.ama-science.org/proceedings.
[33] M. Fritsch, S. Mosch, N. Trofimenko, M. Vinnichenko, M. Kusnezoff „Platinum Nanoinks for Inkjet printed Sensors“, Printed Electronics Konferenz und Messe 2019, IDTechEx Berlin Germany, 10.-11.04.2019.
[32] M. Zea, A. Moya, M. Fritsch, E. Roman, R. Villa, G. Gabriel “Enhanced performance stability of iridium oxide based pH sensors fabricated on rough inkjet-printed platinum”, Journal of Applied Materials and Interfaces, 11, 16, pp.15160-15169. 2019. DOI: doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b03085.
2018
[31] Andreas Albrecht “Printed Sensors for the Internet of Things”, Dissertation Thesis, Technische Universität München, Germany, 2018.
[30] S. Khan, T.P. Nguyen, M. Lubej, L. Thiery, P. Vairac, D. Briand “Low-power printed micro-hotplates through aerosol jetting of gold on thin polyimide membranes” Microelectronic Engineering, 194, pp.71–78, 2018. DOI: doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2018.03.013.
[29] A. Moya, M. Ortega-Ribera, X. Guimerà, E. Sowade, M. Zea, X. Illa, E. Ramon, R. Villa, J. Gracia-Sancho, G. Gabriel “Online oxygen monitoring using integrated inkjet-printed sensors in a liver-on-a-chip system” Lab Chip, 18, pp.2023–2035, 2018. DOI: 10.1039/c8lc00456k.
[28] M. Vinnichenko, M. Fritsch, X. Junchen; D. Makarov, T. Voitsekhivska, V. Sauchuk, M. Kusnezoff “Flexible High-Performance Metallic Interconnects Prepared by Innovative Diode Laser Array Treatment of Inkjet-Printed Layers” Society for Imaging Science and Technology -IS&T-: Printing for Fabrication 2018: Materials, Applications and Processes, 34th International Conference on Digital Printing Technologies (NIP), September 23-27, 2018, Dresden, Germany; Technical Program, Abstracts, and USB Proceedings. Springfield/Va.: IS&T, pp. XIV, 2018.
[27] M. Schubert, Y. Wang, M. Fritsch, M. Vinnichenko, L. Rebohle, T. Schumann, K. Bock „Evaluation of Nanoparticle Inks on Flexible and Stretchable Substrates for Biocompatible Application”, 7th Electronic System-Integration Technology Conference (ESTC) 2018, 18-21. September 2018 Dresden, proceeding in press, IEEE, 2018. DOI: 10.1109/ESTC.2018.8546494.
[26] M. Vinnichenko, D. Makarov, M. Fritsch, T. Voitsekhivska, V. Sauchuk, M. Kusnezoff “Realizing Flexible High-Performance Silver Interconnects on Thin and Ultrathin Substrates by Inkjet-Printing and Innovative Laser Treatment” 14th International Conference on Modern Materials and Technologies (CIMTEC), 04-14.06.2018, Perugia Italy, 2018.
[25] M. Vinnichenko, M. Fritsch, D. Makarov, N. Trofimenko, V. Sauchuk, M. Kusnezoff “Innovative laser processing of inkjet-printed layers” Printed Electronics Europe 2018, IDTechEx, 11.-12.4.2018, Berlin Germany, 2018.
[24] M. Fritsch, M. Vinnichenko, N. Trofimenko, M. Kusnezoff „Metal nanoinks for inkjet printed interconnects on flexible substrates“ LOPE-C 2018, Munich Germany, 14.03.2018, 2018.
2017
[23] J. Stulik and A. Hamacek “Carbon Nanotubes Ammonia Sensor Printed by Aerosol Jet System” 1st PCNS Passive Components Networking Days, 12-15th Sep 2017, Brno, Czech Republic, paper 4.5. New Development Session, PCNS2017 Proceedings pp.91-94. ISBN: 978-80-905 768-8-9.
[22] A. Habermehl, R. Eckstein, N. Strobel, N. Bolse, G. Hernandez.Sosa, A. Mertens, C. Eschenbaum, U. Lemmer „Microfluidic surface-enhanced Raman analysis systems by aerosol jet printing“ IEEE Sensors, Glasgow, United Kingdom, 2017. DOI: 10.1109/ICSENS.2017.8234346.
[21] A. Habermehl, N. Strobel, R. Eckstein, N. Bolse, A. Mertens, G. Hernandez-Sosa, C. Eschenbaum, U. Lemmer „Lab-on-Chip, Surface-Enhanced Raman Analysis by Aerosol Jet Printing and Roll-to-Roll Hot Embossing” Sensors, 17 (10), 2401, 2017. DOI:10.3390/s17102401.
[20] A. Moya, M. Zea, E. Sowade, R. Vila, E. Ramon, R.R. Baumann, G. Gabriel “Inkjet-printed dissolved oxygen and pH sensors on flexible plastic substrates” Proceedings of SPIE Vol. 10246, 102460F, 2017, DOI: 10.1117/12.2264912.
[19] M. Fritsch, M. Vinnichenko, D. Makarov, T. Voitsekhivska, M. Kusnezoff “High-performance silver interconnects prepared on thin and ultrathin flexible substrates by inkjet-printing and laser treatment” Pro Flex 2017 conference, Dresden 27.11.2017, 2017.
[18] M. Fritsch, N. Trofimenko, M. Vinnichenko, V. Sauchuk “Synthesis, formulation and rapid curing of particles based inkjet and aerosoljet printed films for electronic and sensory devices” Poster presented at Printed and Flexible Electronics Congress, London 21-22.2.2017, 2017.
2016
[17] E. Sowade “Inkjet printing of photonic structures and thin-film transistors based on evaporation-driven material transportation and self-assembly” Dissertation Thesis, Technische Universität Chemnitz, Germany, 2016.
[16] M. Fritsch, “Synthesis of particles inks for inkjet printing of microelectronic components” The ICJ 3rd Annual InkJet Conference 2016, Düsseldorf 4.6.10.2016, 2016.
[15] M. Fritsch, M. Vinnichenko “Synthesis And Formulation Of Particle Inks For Inkjet And Aerosol-Jet Printing Methods”, Printed Electronics Europe, New Material – New Possibilities, Berlin April 28, 2016.
[14] A. Moya, E. Sowade, F. J. del Campo, K. Y. Mitra, E. Ramon, R. Villa, R. R. Baumann, G. Gabriel „All-inkjet-printed dissolved oxygen sensors on flexible plastic substrates“, Organic Electronics 39, pp.168-176, 2016, DOI 10.1016/j.orgel.2016.10.002.
[13] M. Zea “Platinum microelectrodes fabricated on flexible substrate by inkjet Printing for pH sensing”, Master’s Thesis, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB), 2016.
[12] M. Fritsch, V. Sauchuk, N. Trofimenko, M. Vinnichenko “Synthesis, formulation and rapidcuring of particles based inkjet and aerosoljetprinted films for electronic and sensory devices” Posterpresented at 2016 MRS Fall Meeting & Exhibit, Boston 27.11.2.12.2016, 2016.
[11] M. Vinnichenko, V. Sauchuk, M. Fritsch, D. Hauschild; N. Trofimenko, M. Kusnezoff “Millisecond laser functionalization of the structures prepared using wet chemical deposition”, 2016 MRS Fall Meeting & Exhibit, Boston 27.11.2.12.2016, 2016.
2015
[10] R. Jurk, M. Fritsch, M. Eberstein, J. Schilm, F. Uhlig, A. Waltinger, A. Michaelis „Ink jet printable silver metallization with zinc oxide for front side metallization for micro crystalline silicon solar cells”, J. Micromech. Microeng. 25, No.12, Art.125021, 7 pp., ISSN: 0960-1317, 2015, DOI: 10.1088/0960-1317/25/12/125021.
[9] R. Soukup, J. Navratil, J. Reboun, T. Rericha “A Comparison of the Interdigital Electrodes Prepared by Aerosol Jet Printing and Lift–Off Technique”, 38th Int. Spring Seminar on Electronics Technology, ISBN 978-1-4799-8860-0, IEEE pp. 30-35, 2015, DOI 10.1109/ISSE.2015.7247956.
[8] S. Hildebrandt, I. Kinski, S. Mosch, A. Waltinger, F. Uhlig, A. Michaelis “Non-contact printing: conductive track geometry affected by ink rheology and composition”, Microsystem Technologies 21, No.6, ISSN: 0946-7076, pp.1363-1369., 2015, DOI 10.1007/s00542-014-2275-8.
2014
[7] R. Jurk, S.Mosch, M.Fritsch, M.Ihle “Synthesis of nano metal particles for low sintering conductive inks”, Fraunhofer Direct Digital Manufacturing Conference 2014 - DDMC, Berlin (12./13.3.2014), E-ISBN: 978-3-8396-9128-1, pp.269-273, 2014, DOI 10.13140/2.1.5044.5766.
[6] M. Eberstein, U. Schmidt, S. Komer, K. Reinhardt, R. Jurk, U. Partsch „In-situ Observations of Glass Frit Related Effects during the Front Side Paste Contact Formation”, Conference: Photovoltaic Specialist Conference (PVSC), ISBN 978-1·4799-4398-2, IEEE, pp. 3463-3469, 2014, DOI: 10.13140/2.1.3068.2567.
[5] N. Trofimenko, S. Mosch, M. Fritsch, R. Jurk, M. Ihle “Metal Nano-inks: From Synthesis to application“, Coating International, 9, pp.16-17, 2014.
2013
[4] K. Swiecinski, M. Ihle, R. Jurk, E. Dietzen, U. Partsch, M. Eberstein “Aerosol jet printing of two component thick film resistors on LTCC”, Additional Conferences (Device Packaging, HiTEC, HiTEN, & CICMT): September 2013, Vol. 2013, No. CICMT, pp. 000240-000246, DOI 10.4071/CICMT-THA25.
[3] M. Neubert, S. Cornelius, J. Fiedler, T. Gebel, H. Liepack, A. Kolitsch, and M. Vinnichenko: Overcoming challenges to the formation of high-quality polycrystalline TiO2: Ta transparent conducting films by magnetron sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 083707, 2013, DOI 10.1063/1.4819088.
vor 2012
[2] M. Fritsch and R. Jurk, “Method for producing nanoparticles from a noble metal and use of the nanoparticles thus produced”, patent application (WO2012/016565A2 and US2013/0205950A1), description of the synthesis of nanoparticles and ink formulation, 2012.
[1] M. Fritsch et al. ”Ink jet printing of fine line metallization with particle Ag inks”, Journal of microelectronics and electronic packaging, IMAPS/ACerS 6th International Conference and Exhibition on Ceramic Interconnect and Ceramic Microsystems Technologies (CICMT, 18.-21.04.2010), Chiba, Japan, 2010.