The purification of particle-polluted exhaust gases at high temperatures (between 250 and 1000 °C) covers a wide range of applications. Major areas of application are the purification of waste gases from the glass and cement industries, from waste incineration plants and biomass gasification, as well as dust removal from gas, steam and combined cycle power plants. Other important applications are in the recovery of valuable materials from catalysts, fumed silica and metal powders. Due to the special filtration conditions and the special requirements on the properties and resistance of the materials, it represents a separate area of filtration.
Ecological and economic advantages of hot gas filtration
The use of high temperatures in waste gas purification offers many advantages, not only from an environmental point of view, but also from an economic point of view.
By utilizing the high temperature level, cooling and reheating processes for subsequent reactions and plant components can be avoided. This in turn leads to a beneficial increase in efficiency of the overall process and offers the possibility of process simplification. Hot gas filters are advantageously used to protect and maintain the efficiency of downstream plant modules. For example, heat exchangers, catalysts, turbines and scrubbers are protected from dust and can operate efficiently due to the high temperature level. Possible condensation and desublimation processes can be avoided, which can protect the filters from blockages and the end product from unwanted contamination. Some processes are only made possible by using hot gas filters, such as phosphorus recovery in sewage sludge incineration and biomass gasification and pyrolysis. Also, the recirculation of material flows or process gases as well as product and material recovery in high-temperature processes can be realized without great additional effort and high energy input.
In order to further push the possibilities and limits, Fraunhofer IKTS is researching and optimizing materials, technologies and processes in the field of hot gas filtration.
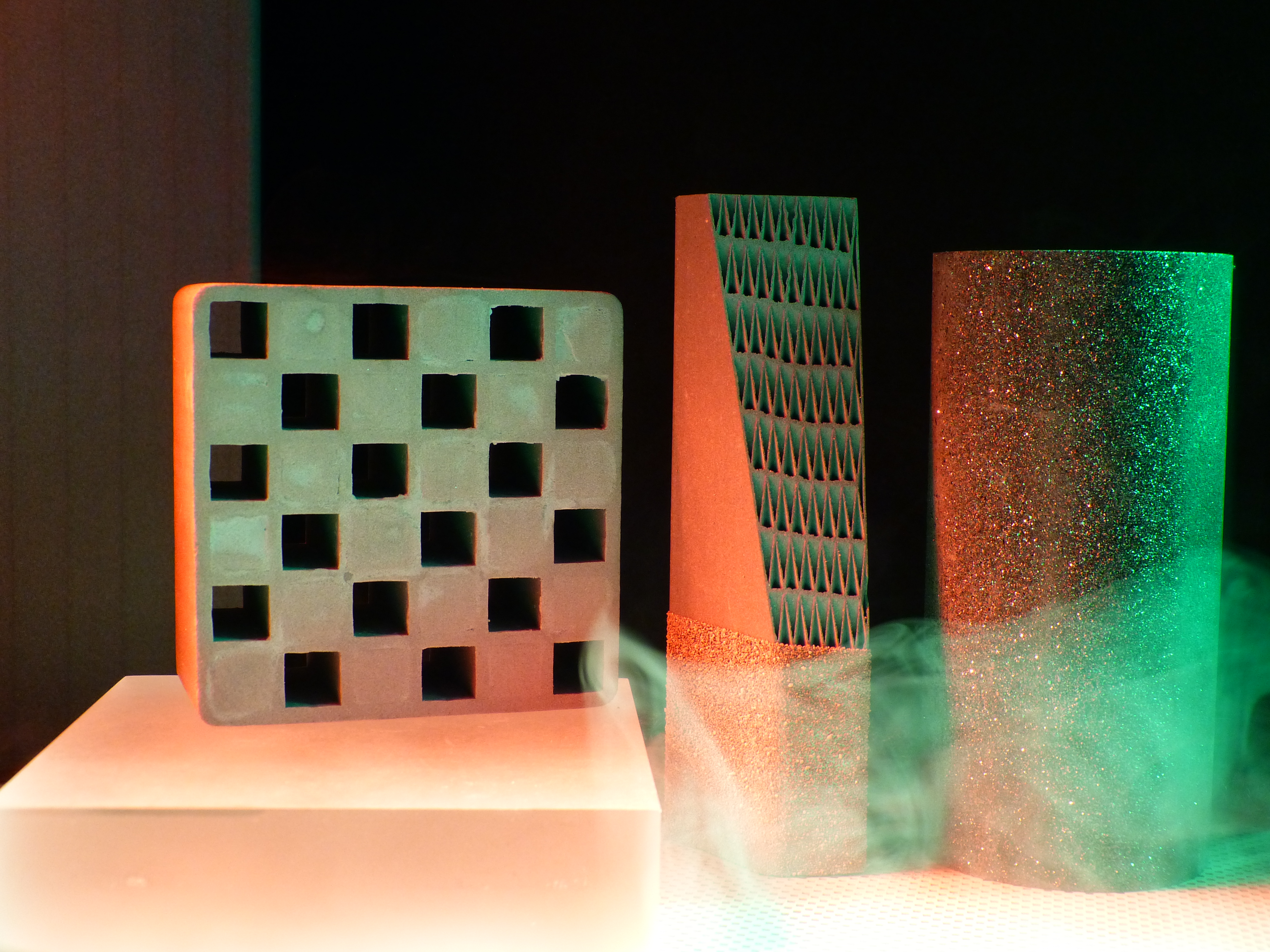
Ceramic filter materials
Ceramic hot gas filter elements are used primarily when conventional or synthetic fabric filters reach their performance limits in cleaning particle-polluted exhaust gases. At temperatures above 800 °C and under very corrosive conditions, hot gas filters made from silicon carbide (SiC) are particularly suitable due to their thermal and chemical resistance. Other materials frequently used are aluminum oxide and cordierite. Good thermal conductivities or low co-efficients of thermal expansion form the basis for good thermal shock resistance of many ceramics, which makes these materials ideal for use under cyclic stresses. SiC hot gas filters are often able to offer cost-effective alternatives to expensive special alloys for filtering exhaust gases up to 1000 °C.
Services offered
- Development, testing and optimization of materials for hot gas filtration (silicon carbide, alumina, ferrous and non-ferrous metals)
- Filter production from powder to component (sample and small-series production)
- Material characterization and component testing from room temperature to 1000 °C (material composition, pore characteristics, differential pressure behavior, filtration efficiency, strength, corrosion resistance)
- Endurance tests on the hot gas test stand for aging, filter regeneration and filter efficiency
- Post-mortem analyses of hot gas filters
- Design and optimization of hot gas filters
- Targeted exhaust gas aftertreatment for thermal combustion processes, especially for the recovery of valuable materials
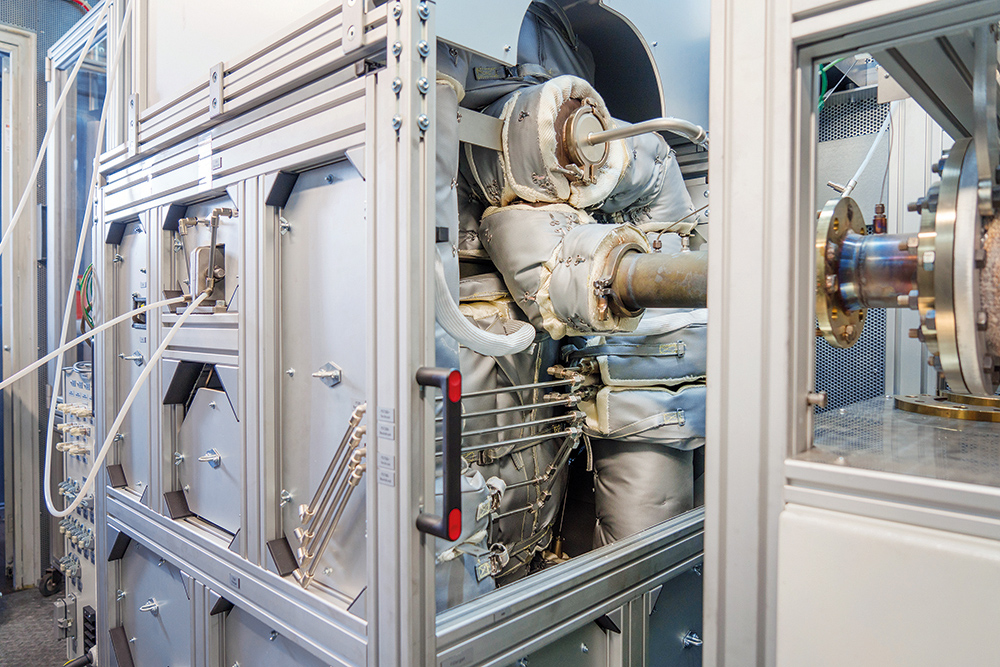
Technical equipment
The loads in high-temperature applications are often very complex, so that in most cases testing under application conditions is indispensable. For the material development of the filter elements, catalytic and adsorptive coatings for the reduction of nitrogen oxides and other pollutant gases, special high-temperature test stands were set up that allow the ceramics to be tested under conditions that are very close to the application:
- Industrial hot gas filtration test stand up to 1000 °C for endurance testing of filters or cyclic tests for lifetime prediction
- Dusting, back pressure and particle test stand for segments and filter discs at room temperature
- Dusting, backpressure and particle test stand for wall-flow filters in hot gas up to 1000 °C
- Backpressure measurements up to 12 bar on small sample geometries (porometer)
- Pressure drop test stand for foam ceramics up to 20 m/s
- Catalysis test stands for the investigation of chemical adsorption and temperature-programmed reactions on powder samples
- Synthesis gas test stands for the investigation and aging of honeycomb bodies and drill core samples in static and highly dynamic operating regimes
- Further measuring instruments and analysis devices for the characterization of filters and filter systems
Examples and references
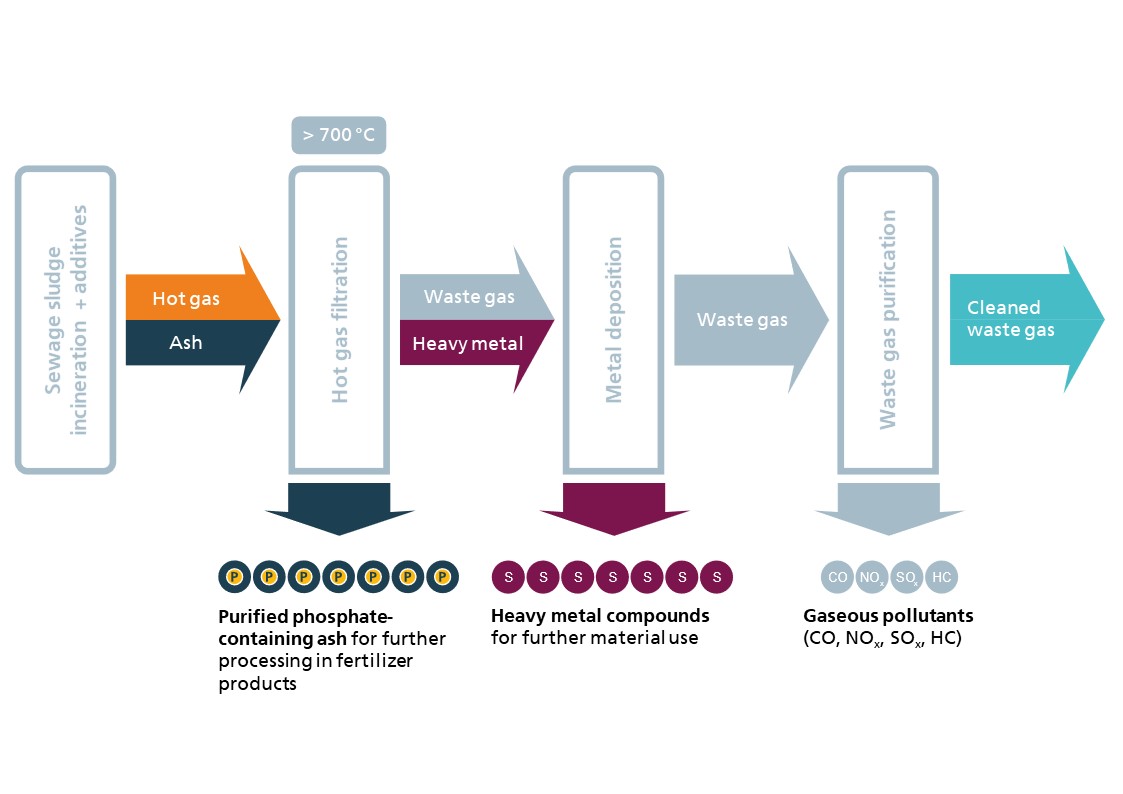
- Establishment of hot gas filters and hot gas filtration for the recovery of phosphorus and heavy metals during sewage sludge incineration (abonocare®)
- Development and demonstration of hot gas filtration for economical sewage sludge incineration and phosphorus recovery to close regional nutrient cycles (DreiSATS)
- Development and demonstration of a hot gas filtration plant for the dedusting of exhaust gases from steel, lime and dolomite plants (CO2-Selekt)
- Development of hot gas filters and processes for the recycling and reuse of materials down to the molecular level (Molecular Sorting)